Abstract
Search intelligence is evolving from Deep Research to Wide Research, a paradigm essential for retrieving and synthesizing comprehensive information sets under complex constraints in parallel. However, advancements in this field are impeded by the lack of dedicated benchmarks and optimization methodologies for search breadth. To address these challenges, we give a deep dive into Wide Research from two perspectives: Data Pipeline and Agent Optimization. First, we produce WideSeekBench, a General Broad Information Seeking (GBIS) benchmark constructed via a rigorous multi-phase data pipeline to ensure diversity across the volume of target information, logical constraints, and domains. Second, we introduce WideSeek, a dynamic hierarchical multi-agent architecture that could autonomously fork parallel sub-agents based on task requirements. Furthermore, we design a unified training framework that linearizes multi-agent trajectories and optimizes the system using end-to-end RL. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of WideSeek and multi-agent RL, highlighting that scaling the number of agents is a promising direction for advancing Wide Research paradigm.
Key Contributions
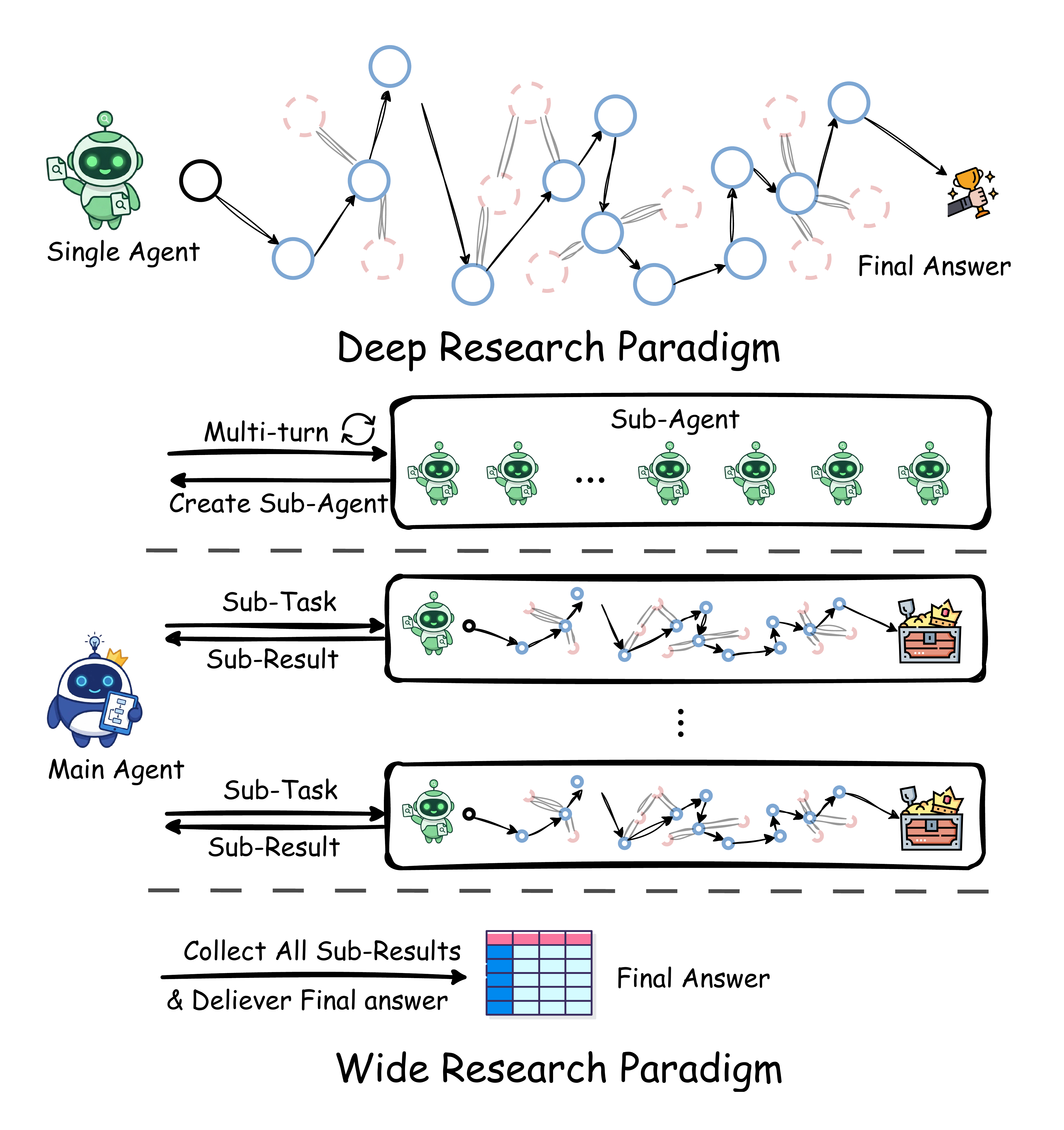
Deep Research paradigm v.s. Wide Research paradigm.
📊 WideSeekBench
A General Broad Information Seeking (GBIS) benchmark constructed via a rigorous multi-phase data pipeline, ensuring diversity across information volume, logical constraints, and domains.
🤖 WideSeek Architecture
A dynamic hierarchical multi-agent system that autonomously forks parallel sub-agents based on task requirements, enabling scalable information retrieval.
🎯 Unified RL Framework
An end-to-end reinforcement learning framework that linearizes multi-agent trajectories and optimizes the system for wide research tasks.
Method Overview
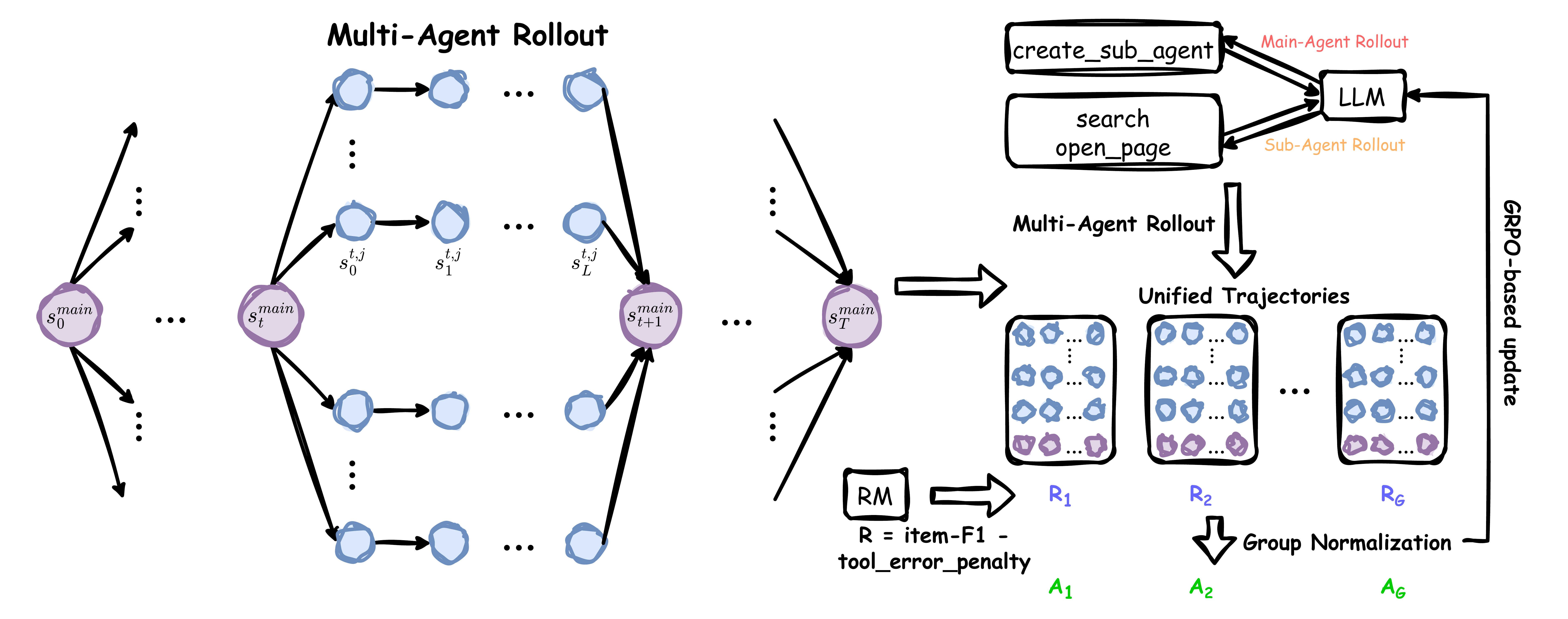
An illustration of Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning. As shown on the left, the main agent can fork any number of sub-agents at any step. The trajectories of the main agent and sub-agents are unified for RL training.
Dynamic Multi-Agent Architecture
WideSeek operates as a hierarchical multi-agent system with a centralized Main Agent (Planner) that dynamically forks variable instances of Sub-Agents (Executors) at any step. Unlike static multi-agent architectures with fixed roles, WideSeek empowers the main agent with complete autonomy to instantiate any number of sub-agents based on task requirements.
Unified Reinforcement Learning
We linearize the hierarchical execution trace into a single sequence and optimize the system using Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO). The unified trajectory interleaves Main Agent planning steps with Sub-Agent execution steps, enabling end-to-end optimization of the entire multi-agent system.
WideSeekBench
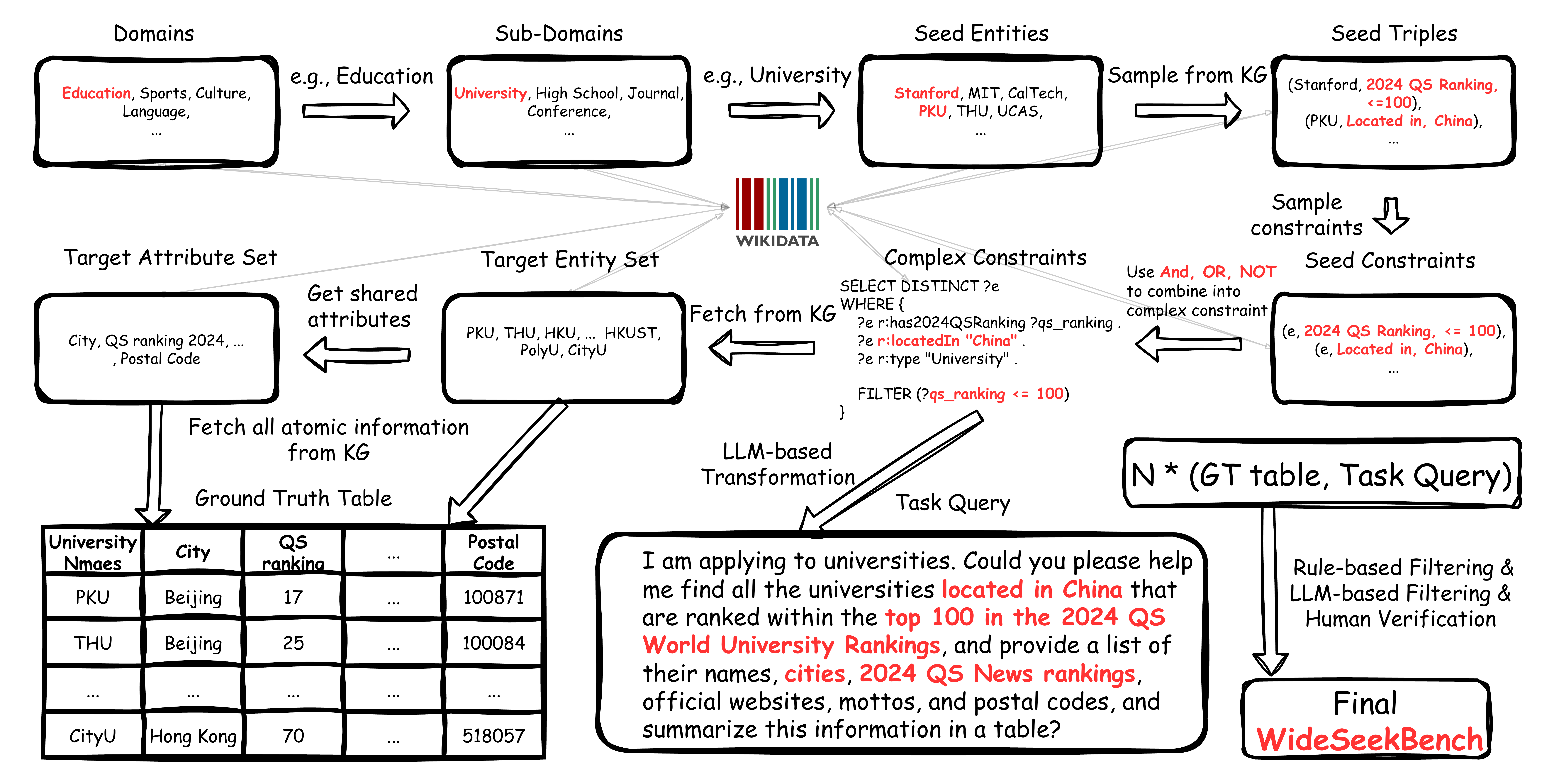
The data pipeline of WideSeekBench constrauction, whcih mines a set of target information under complex constraints.
WideSeekBench is a General Broad Information Seeking (GBIS) benchmark constructed via a rigorous multi-phase data pipeline. The benchmark ensures diversity across:
- Volume of target information: Varying scales of information retrieval tasks
- Logical constraints: Complex set operations (intersection, union, difference)
- Domains: Multi-dimensional domain coverage
Experimental Results
Main Results on WideSeekBench
| Model | Success Rate (%) | Row F1 Score (%) | Item F1 Score (%) | # Sub-Agents | # Tool Calls | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean@4 | Max@4 | Mean@4 | Max@4 | ||||
| Proprietary Models | |||||||
| GPT-5.2 | 0.00 | 4.45 | 6.75 | 21.03 | 26.88 | 11.21 | 408.64 |
| GPT-5.1 | 0.00 | 4.11 | 6.75 | 20.44 | 27.88 | 6.02 | 121.36 |
| DeepSeek-v3.2 | 0.00 | 4.34 | 6.85 | 20.51 | 27.09 | 31.25 | 326.41 |
| Kimi-K2-Thinking | 0.00 | 3.17 | 5.86 | 17.48 | 25.19 | 8.74 | 85.36 |
| Seed-1.8 | 0.14 | 3.44 | 5.92 | 17.88 | 25.23 | 7.93 | 88.36 |
| Open-Sourced Models | |||||||
| Qwen3-8B-Thinking | 0.00 | 0.53 | 1.51 | 7.37 | 12.71 | 4.18 | 9.50 |
| Qwen3-30B-A3B-Thinking | 0.00 | 1.26 | 3.00 | 10.11 | 16.51 | 7.53 | 17.15 |
| WideSeek-8B-RL | 0.00 | 1.09 (+0.56) | 2.59 (+1.08) | 10.86 (+3.49) | 16.61 (+3.90) | 9.57 (×2.29) | 41.09 (×4.33) |
| WideSeek-8B-SFT | 0.14 | 1.74 (+1.21) | 3.66 (+2.15) | 11.35 (+3.98) | 18.92 (+6.21) | 13.16 (×3.15) | 121.98 (×12.84) |
| WideSeek-8B-SFT-RL | 0.00 | 1.95 (+1.42) | 3.88 (+2.37) | 12.87 (+5.50) | 19.73 (+7.02) | 26.60 (×6.36) | 273.75 (×28.82) |
Experiment results on WideSeekBench. We run each task for 4 times.
The training dynamics of WideSeek-8B-RL. We present the evolution of training rewards and the frequency of tool calls throughout the entire training process.
Generalization to Deep Research
To assess whether the capabilities transfer to deep research tasks, we evaluate our models on the BrowseComp-Plus dataset.
| Model | Scaffold | Acc (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Baseline Models (ReAct) | ||
| Gemini-2.5-Pro | ReAct | 29.52 |
| GPT-OSS-120B-Low | ReAct | 25.54 |
| DeepSeek-R1-0528 | ReAct | 16.39 |
| Search-R1-32B | ReAct | 11.08 |
| Qwen3-32B | ReAct | 10.72 |
| WideSeek Models | ||
| Qwen3-30B-A3B | WideSeek | 14.82 |
| Qwen3-8B | WideSeek | 14.22 |
| WideSeek-8B-SFT | WideSeek | 23.61 |
| WideSeek-8B-SFT-RL | WideSeek | 23.61 |
| WideSeek-8B-RL | WideSeek | 26.42 (+12.20) |
BrowseComp-Plus performance. We test the generalization of WideSeek to Deep Research dataset.
Key Findings
- Scalability: WideSeek-8B-SFT-RL achieves 28.82× increase in tool calls and 6.36× increase in sub-agent instantiation compared to base model.
- Performance: Item F1 score of 12.87% (+5.50% over base) and Max Row F1 of 3.88% on WideSeekBench.
- Generalization: Achieves 26.42% accuracy on BrowseComp-Plus (+12.20% improvement), demonstrating transfer to Deep Research tasks.
- Efficiency: The system learns to scale search effort aggressively, with strong correlation between reward and tool usage.
Analysis
Item-F1 score, the number of sub-agents, and the number of tool calls on different task sets with different volume of target information.
Item-F1 score on different domains.
Item-F1 score on different constraint types.
BibTeX
@misc{huang2026wideseekadvancingwideresearch,
title={WideSeek: Advancing Wide Research via Multi-Agent Scaling},
author={Ziyang Huang and Haolin Ren and Xiaowei Yuan and Jiawei Wang and Zhongtao Jiang and Kun Xu and Shizhu He and Jun Zhao and Kang Liu},
year={2026},
eprint={2602.02636},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CL},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2602.02636},
}